数据类型
标量和向量
- 标量: 只有一个数, 不具有方向性, 比如说NumPy的nd数组中的一个元素
- 向量: 由标量组成, 具有方向性, 比如说NumPy的nd数组
标量和向量属性的一致性
在NumPy中, 为了消除混合标量和nd数组操作时产生的不一致性, 我们将nd数组(向量)中的元素(标量)也视为一个nd数组(向量), 这可以通过保持标量和向量的属性一致实现, 也就是说由np.[type]([value])创建的标量具有和向量相同的属性和方法.
正因为如此, 我们可以称由np.[type]([value])创建的标量特别的称为"数组标量". 更多的属性可以在这里找到, 更多的方法可以在这里找到.
例子
np.[type]类
np.[type]是一个类, np.[type]([value])用于创建标量, 或"数组标量".
Tip
Python自带的int也是一个类,由int创建的对象是Python标量, 不是数组标量. 这两种标量的属性有很大不同.
例子
别名类
| 名称 | C语言中的类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
np.int_ |
long |
一般是np.int32或np.int64(取决于系统是32位还是64位) |
np.intc |
int |
一般是np.int32或np.int64(取决于系统是32位还是64位) |
np.intp |
ssize_t |
一般是np.int32或np.int64(取决于系统是32位还是64位) |
np.float_ |
double |
float64类型的简写 |
np.complex_ |
double complex |
complex128类型的简写 |
固定类
| 名称 | C语言中的类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
np.bool_ |
bool |
布尔数据类型 |
np.int8 |
int8_t |
整数 -128 ~ 127 |
np.int16 |
int16_t |
整数 -32768 ~ 32767 |
np.int32 |
int32_t |
整数 -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 |
np.int64 |
int64_t |
整数 -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 |
np.uint8 |
uint8_t |
无符号整数 0 ~ 255 |
np.uint16 |
uint16_t |
无符号整数 0 ~ 65535 |
np.uint32 |
uint32_t |
无符号整数 0 ~ 4294967295 |
np.uint64 |
uint64_t |
无符号整数 0 ~ 18446744073709551615 |
np.float16 |
无 | 半精度浮点数, 包括: 1个符号位, 5个指数位, 10个尾数位 |
np.float32 |
float |
单精度浮点数, 包括: 1个符号位, 8个指数位, 23个尾数位 |
np.float64 |
double |
双精度浮点数, 包括: 1个符号位, 11个指数位, 52个尾数位 |
np.complex64 |
float complex |
复数, 表示双32位浮点数(实数部分和虚数部分) |
np.complex128 |
double complex |
复数, 表示双64位浮点数(实数部分和虚数部分) |
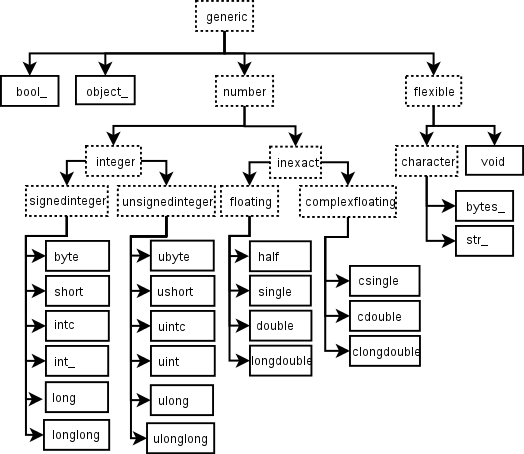
层级
np.[type]类有一个层次结构来表示继承关系.
例子
np.dtype类
np.dtype是一个类, 由np.dype([base_type])创建的对象被用来表示nd数组中元素或者数组标量的类型, 类似于C语言中的结构体, 可以定义基类, 定义字节数量, 定义是小端还是大端等等. 我们可以通过对象的type属性知道它的基类.
注意
- 在创建数组标量的时候, 其
dtype属性会被自动赋值为一个np.dtype([type])对象. 详情见这里. - 在创建nd数组的时候, 其
dtype属性会被自动赋值为一个np.dtype(np.float64])对象, 或者也可以手动赋值.
例子
-
NumPy 数据类型 | 菜鸟教程. (n.d.). From https://www.runoob.com/numpy/numpy-dtype.html ↩
-
Data type objects (dtype)—NumPy v2.0 Manual. (n.d.). From https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.dtypes.html ↩
-
Scalars—NumPy v2.0 Manual. (n.d.). From https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.scalars.html ↩